Background
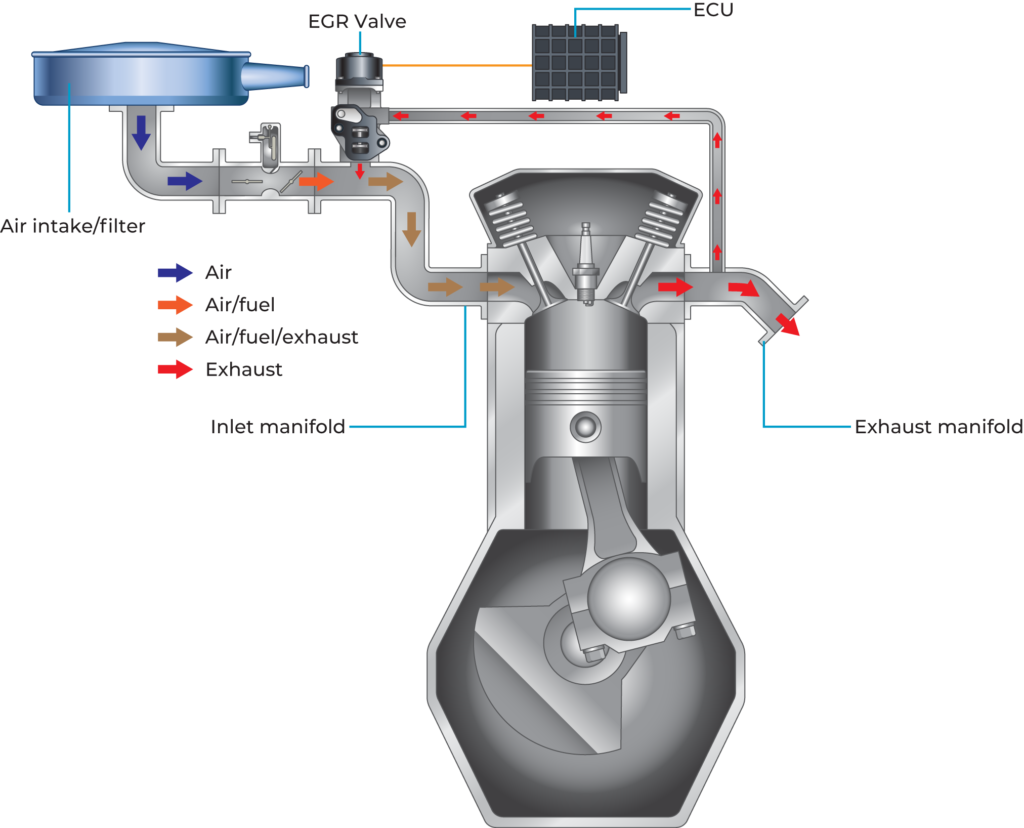
The EGR System, or Exhaust Gas Recirculation System, is designed to force exhaust gasses back into the engine, reducing the temperature of the combustion and burning any unspent fuel. This, combined with other emissions systems, reduces the amount of harmful gasses released into the atmosphere. Vehicle owners often tamper with the EGR System, and the aftermarket supplies numerous pre-manufactured components to assist.
EGR Valves are often removed on performance vehicles to increase horsepower and fuel economy. A simple plate, known as a “block-off plate” is installed to fill the gap where an EGR valve was removed. Any time flow is restricted, horsepower is decreased. The EGR valve cools the temperature of the combustion, reducing efficiency and horsepower.
Removing the EGR valve will trip the sensors in a car from 2001 or newer. In cars older than 2001, a visual inspection must be performed to make sure the EGR valve is installed and in working order. A vehicle may fail the visual inspection if the EGR is present, but hoses or sensors are disconnected.
If a vehicle fails smog because of high NOX, their EGR Valve may be clogged or dysfunctional. Explain the failed test to the customer and refer them to a 2G smog for their repairs.
